About Ecuador
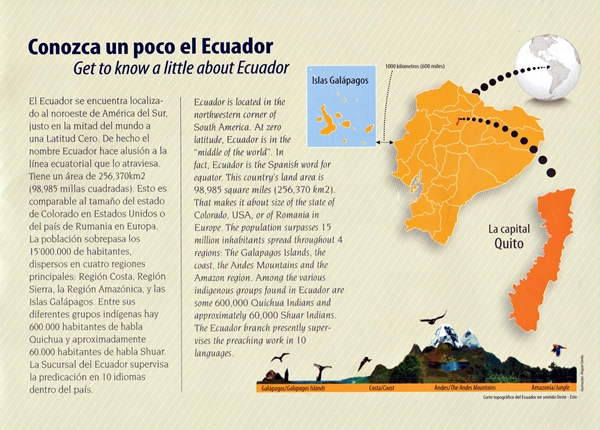
Ecuador is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Ecuador also includes the Galápagos Islands in the Pacific, about 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) west of the mainland.
Spanning an area of 283,520 km2, and with a population of 15.2 million, Ecuador is home to a variety of indigenous groups, including mostly Spanish descent, followed by large minorities of European, Amerindian, and African descendants.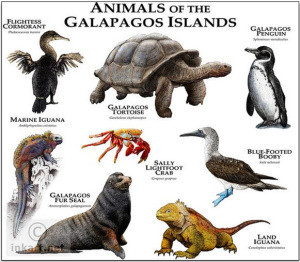
Language: Spanish is the official language and is spoken by a majority of the population, though thirteen indigenous languages are also recognized, including Quichua and Shuar. The capital city is Quito (203 million population,) while the largest city is Guayaquil (2.7 million.)
Ecology: Ecuador is also known for its rich ecology, hosting many endemic plants and animals, such as those of the Galápagos Islands. The geography of Ecuador includes the coastal region, tropical jungle and rainforest regions, as well as the Andes mountain and volcanic regions.
Climate: There is great variety in the climate, largely determined by altitude. It is mild year-round in the mountain valleys, with a humid subtropical climate in coastal areas and rainforest in lowlands. The climate in the Andean highlands is temperate and relatively dry, and the Amazon basin on the eastern side of the mountains shares the climate of other rainforest zones.
Equator: Because of its location at the equator, Ecuador experiences little variation in daylight hours during the course of a year. Both sunrise and sunset occur each day at around 6 am and 6 pm.
Volcanoes: Ecuador is also home to the highest active volcano in the world, Cotopaxi, at 19,347 feet. Just 30 miles south of Quito, on a clear day, it can be seen easily from the city.
Pichincha (over 15,000 ft) is a smaller active volcano sitting at the very edge of Quito. An eruption in 1999, covered the city in several inches of ash.